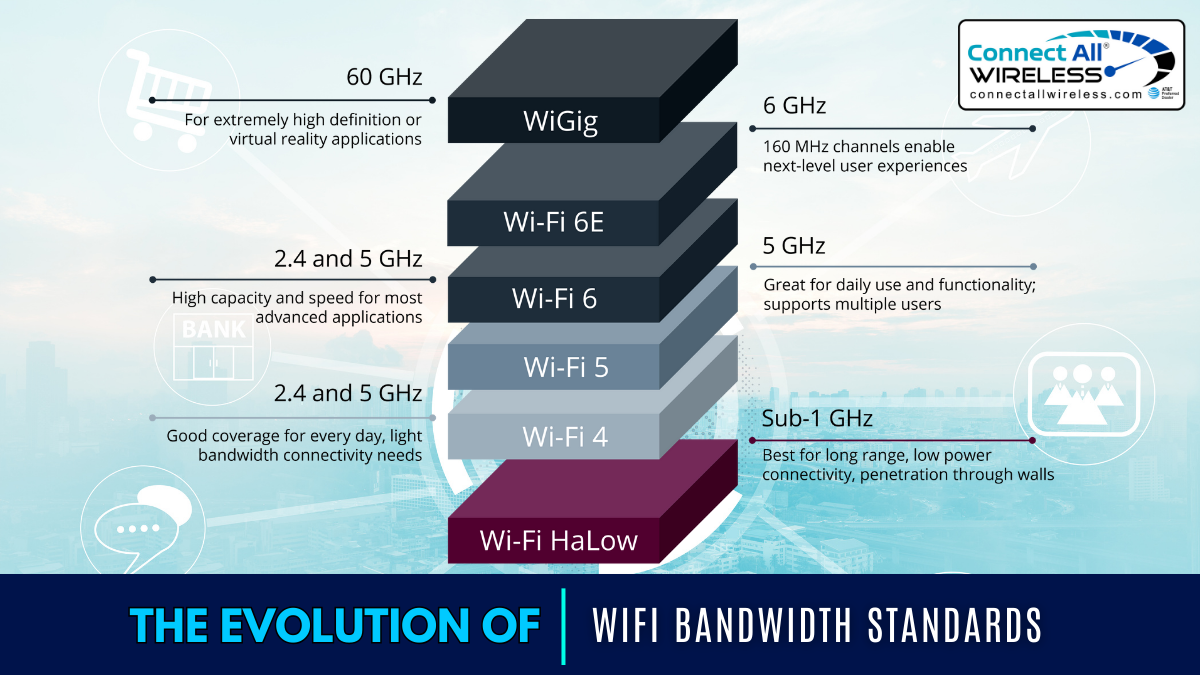
The Evolution of WiFi Bandwidth Standards
January 3, 2024In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, WiFi has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. As technology advances, so does the evolution of WiFi standards, aiming to meet the escalating demands for faster, more reliable, and secure wireless connectivity. Let’s delve into the journey of WiFi bandwidth standards, from the early days to the latest advancements.
WiFi 4 (802.11n)
Introduction to the Shift: WiFi 4, also known as 802.11n, marked a significant leap forward in wireless networking. It introduced Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology, enabling faster speeds and increased range compared to its predecessors.
Key Features:
- Speed Boost: Offering maximum speeds of up to 600 Mbps, WiFi 4 enhanced the user experience by delivering faster data rates.
- Improved Range: With multiple antennas, it provided better coverage and signal strength, minimizing dead zones.
WiFi 5 (802.11ac)
Advancements and Performance: WiFi 5, or 802.11ac, brought substantial improvements over WiFi 4. It introduced wider channels, MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output), and beamforming technologies.
Key Features:
Gigabit Speeds: Capable of delivering speeds exceeding 1 Gbps, WiFi 5 revolutionized streaming, gaming, and data-intensive tasks.
Enhanced Capacity: MU-MIMO enabled simultaneous connections to multiple devices, optimizing network performance in crowded environments.
WiFi 6 (802.11ax)
Next-Level Connectivity: WiFi 6, also referred to as 802.11ax, represented a paradigm shift in wireless networking, focusing on efficiency, capacity, and performance improvements.
Key Features:
Increased Efficiency: Utilizing OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) technology, WiFi 6 efficiently handles multiple device connections, reducing latency and congestion.
Enhanced Speed and Range: Offering speeds beyond 9 Gbps and improved coverage, WiFi 6 caters to the growing demands of smart homes and businesses.
WiFi HaLow (802.11ah)
Catering to IoT and Low-Power Devices: WiFi HaLow, or 802.11ah, was designed to address the specific needs of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, focusing on extended range and lower power consumption.
Key Features:
Extended Range: Operating in the 900 MHz frequency band, WiFi HaLow offers increased coverage, making it suitable for IoT devices spread across large areas.
Low Power Consumption: Optimized for devices requiring minimal power, it enables prolonged battery life in sensors and IoT gadgets.
WiGig 60GHz (802.11ad)
Ultra-Fast, Short-Range Connectivity: WiGig 60GHz, or 802.11ad, aimed to deliver ultra-fast speeds over short distances, ideal for specific applications requiring high bandwidth.
Key Features:
Extreme Speeds: Operating in the 60 GHz frequency band, WiGig enables speeds up to 7 Gbps, facilitating rapid data transfers for applications like wireless docking and VR.
Limited Range: Due to its high frequency, WiGig’s coverage is restricted to shorter distances, limiting its use to specific scenarios.
WiFi 6E (802.11ax-2021)
Expanding into the 6GHz Spectrum: WiFi 6E is an extension of WiFi 6, utilizing the newly opened 6GHz frequency band to alleviate congestion and provide additional bandwidth.
Key Features:
Increased Bandwidth: Leveraging the 6GHz spectrum, WiFi 6E offers broader channels, reducing interference and enabling faster speeds for applications demanding high bandwidth.
Reduced Congestion: With access to a new spectrum, WiFi 6E devices can operate in less crowded frequencies, improving overall network performance.
Conclusion
In summary, the journey through the evolution of WiFi bandwidth standards has been nothing short of transformative, shaping the way we connect and communicate. From the foundational WiFi 4 to the cutting-edge WiFi 6E, each standard has contributed to the seamless integration of high-speed WiFi internet. This evolution is particularly significant for places like Michigan, where the demand for robust connectivity is on the rise. As technology continues to advance, the state is poised to benefit from the latest standards, ensuring that residents and businesses alike can enjoy the advantages of high-speed, reliable WiFi.
The ongoing commitment to staying at the forefront of WiFi technology underscores the importance of keeping pace with the evolving needs of a digitally connected society, and in Michigan, the journey towards high-speed WiFi internet is an integral part of this technological progression. As we embrace the future of connectivity, the evolution of WiFi bandwidth standards stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of faster, more efficient, and accessible internet for all, ensuring that Michigan remains at the forefront of the digital era.